Home
Focus Areas
Our independent analyses of the complex interactions among co-evolving systems aid decision-makers in confronting multiple, interwoven challenges.
Research Tools
Our state-of-the-art models and analytical methods project global and regional changes and potential risks under different policy scenarios.
Simulates the interplay between Earth and human systems
Simulates physical, dynamical and chemical processes in the atmosphere, land, ocean and cryosphere
Simulates the evolution of economic, demographic, trade and technological processes
Analytical methods to quantify uncertainty at global and regional scales
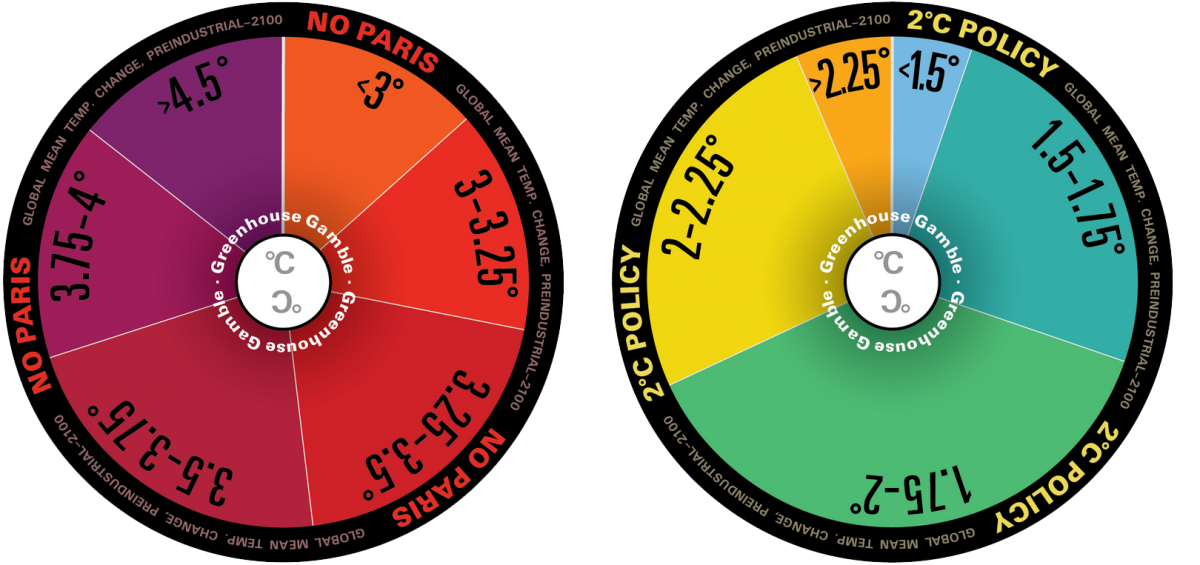
Global Change Outlook
Our Greenhouse Gamble Wheels
News

MIT Joint Program Co-Director Emeritus John Reilly highlights key challenges (Associated Press)

Emissions are attributed to the country where they happen geographically—even if the energy produced, or the products manufactured, are destined for somewhere else (MIT Climate Portal)

Knowing where to look for this signal will help researchers identify specific sources of the potent greenhouse gas (MIT News)